Find What You Need, Fast: A Guide to Sorting and Filtering
Feeling overwhelmed by lists of data? With Smackdab's powerful sorting and filtering tools, you can instantly organize your view to see exactly what matters most.
Sorting puts your data in order. Think A-Z, 1-100, or newest to oldest.
Filtering hides what you don't need to see, letting you focus on a specific group of records.
Used together, they are your secret weapons for managing your pipeline and making smart, data-driven decisions. Let's dive in!
How to Sort Your Data
Need to see your highest-value deals at the top of the list? Sorting lets you reorder any list in just a few clicks.
-
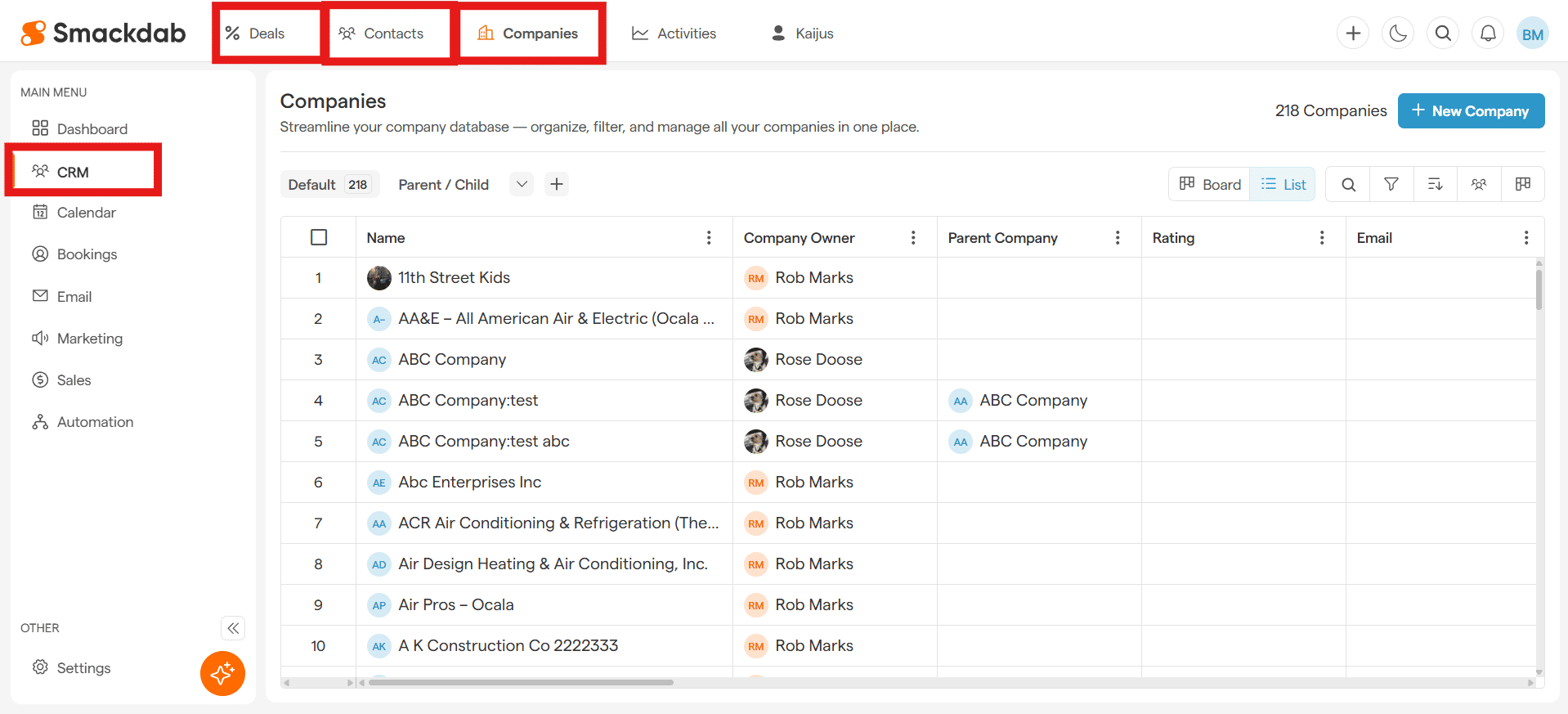
Navigate to a list view.
From the CRM section in the main menu, select Deals, Contacts, or Companies.
-
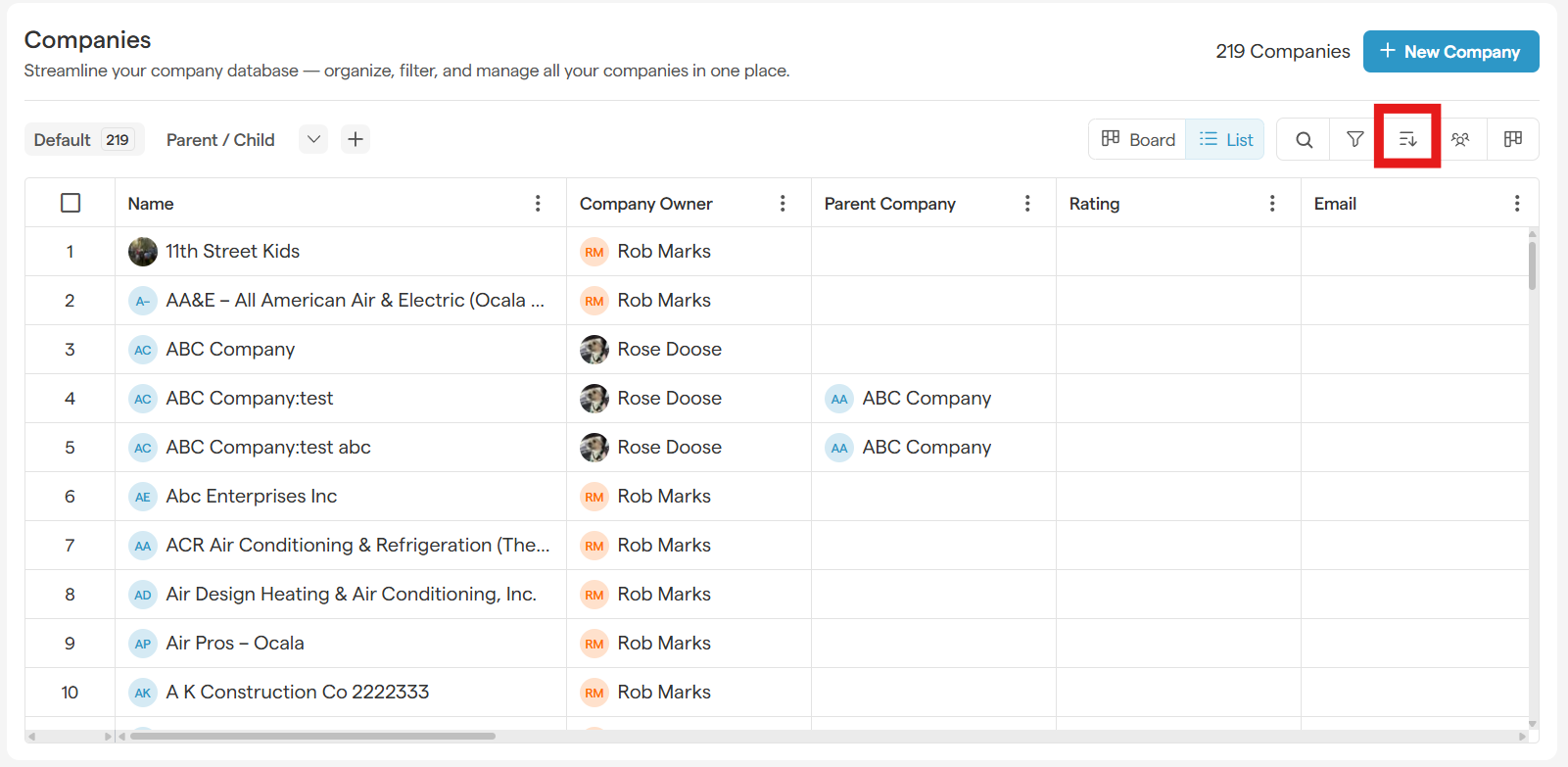
Above the list, click the Sort button.
-
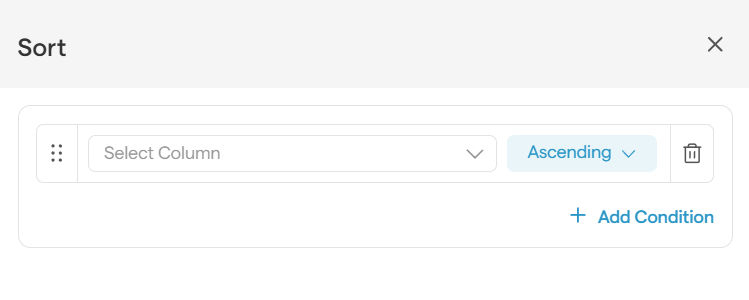
In the panel, select the column you want to sort by (e.g., "Deal Value").
Choose whether you want to sort in Ascending (A-Z, 1-100) or Descending (Z-A, 100-1) order.
Click Save, and your list will instantly rearrange!
Pro-Tip: Need to sort by more than one thing? Click the + Add Condition button to add another sorting rule, like sorting by deal value first, then by close date.
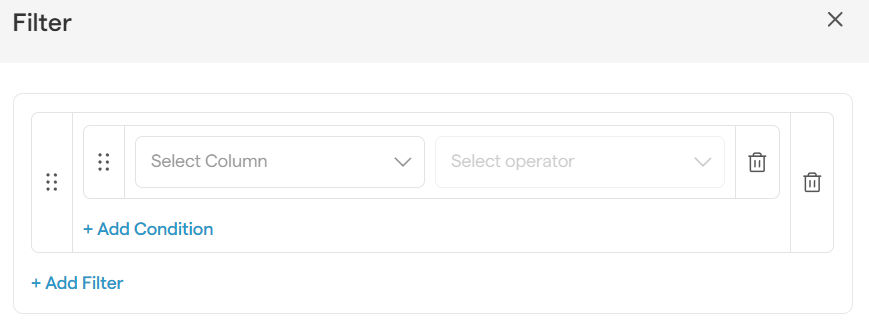
How to Filter Your Data
Filtering is how you narrow your focus to a specific segment of your data, like seeing only the deals in the "Negotiation" stage.
-
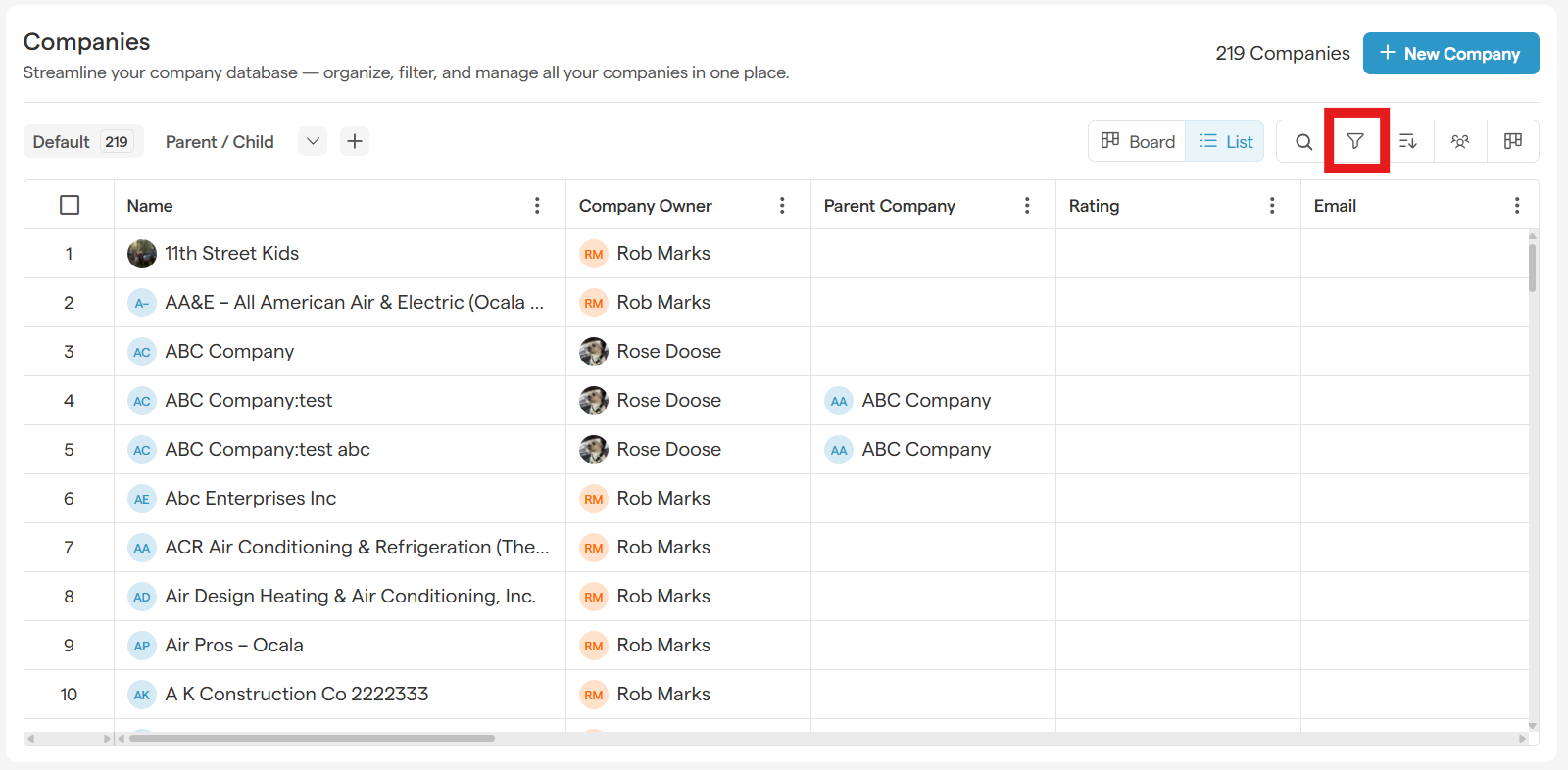
From any module's main list page, click the Filter button.
-
In the panel, you'll build your rule:
Select a column to filter by (e.g., "Stage").
Select an operator (e.g., "is equal to").
-
Enter or select a value (e.g., "Negotiation").
Click Save to apply the filter and watch your list shrink to show only what matches your rule.
Want to get even more specific? Click the + Add Filter button to add another filter and narrow your results further.
Power Play: Combine Filters and Sorting
Here's where the magic happens. A sales rep could filter their deals to see only those in the "Negotiation" stage, and then sort that filtered list by "Deal Value" in descending order. In seconds, they have a prioritized list of their most valuable, late-stage deals.
Your Complete Filter Toolkit
When you build a filter, you have a wide range of conditions (or "operators") to choose from. Here’s a guide to what they do:
Filtering by Text (e.g., Name, Company)
Contains: The field includes your specified text.
Does not contain: The field does not include your text.
Starts with / Ends with: The field begins or ends with your text.
Equal to / Not equal to: The field exactly matches (or does not match) your text.
Empty / Not Empty: The field is either blank or has any text in it.
Filtering by Numbers (e.g., Deal Value, Employee Count)
Equal to (=) / Not equal to (!=)
Greater than (>) / Greater than or equal to (>=)
Less than (<) / Less than or equal to (<=)
Empty / Not Empty: The number field is either blank or has a value.
Filtering by Dates (e.g., Close Date, Last Activity)
For any date field, a handy calendar and time picker will appear to help you select your values.
Equal to / Not equal to: Matches (or doesn't match) a specific date.
Before / After: Is earlier or later than a specific date.
Between / Not in Range: Falls within or outside of a specific date range.
Is set / Is not set: The date field either has a value or is empty.
-
Relative Dates: This is a powerful one! Filter by dynamic timeframes like:
Today / Yesterday
This Week / This Month / This Quarter / This Year
Last 7 Days / Last 30 Days
Last Week / Last Month / Last Quarter / Last Year
Filtering by Yes/No Fields (e.g., "Subscribed")
Is true / Yes
Is false / No